
Premature ejaculation (PE) is one of the most common male sexual dysfunctions, affecting approximately 20–30% of men in Taiwan, particularly those in their 20s and 30s. PE may lead to additional issues such as erectile dysfunction, increased psychological stress, sexual anxiety, lowered self-esteem, depression, and strained relationships.
Anatomy: Dorsal Nerve of the Penis
The dorsal nerve of the penis, the deepest branch of the pudendal nerve (S2–S4), travels along the pelvic wall and emerges through the pudendal canal. It gives rise to the perineal nerve and the dorsal nerve, which runs along the inferior pubic ramus and between the layers of the urogenital diaphragm, ultimately reaching the glans penis (Figure 1).
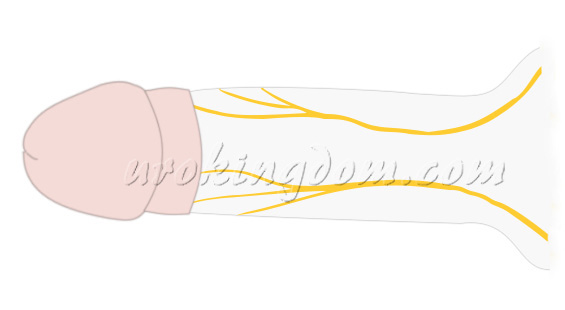
SDN Surgery: Principle & Rationale
The exact cause of PE is not fully understood, but both psychological and biological factors contribute, including anxiety, hypersensitivity of the dorsal nerve, and serotonin receptor dysfunction.
Studies show that PE patients have lower vibration thresholds, indicating increased penile sensitivity. Some reports also suggest these patients have more dorsal nerve branches than average, leading to heightened sensitivity. Reducing this sensitivity can potentially delay ejaculation.
When medications or behavioral therapies fail, Selective Dorsal Neurotomy (SDN) offers a surgical alternative. It involves partial denervation of the penile dorsal nerve to reduce sensitivity and prolong intravaginal ejaculation latency time (IELT), without negatively impacting sexual satisfaction.
Originally introduced by Tullii RE in 1993, SDN has gained popularity and is now widely practiced in various countries, supported by increasing clinical research.
Can SDN Be Combined with Circumcision?
Yes. Some studies suggest circumcision may help delay ejaculation by keratinizing the glans and reducing sensitivity. For patients with phimosis or excessive foreskin, combining circumcision with SDN may offer added benefits: less swelling, improved hygiene, and reduced STD risk.
Minimally Invasive SDN Procedure
Our clinic has improved upon traditional SDN methods to develop a minimally invasive microsurgical approach performed under dual-local anesthesia.
Surgical Steps:
- The incision is closed with absorbable micro-sutures
- A ring-shaped incision is made below the glans
- The foreskin is retracted and internal fascia carefully dissected
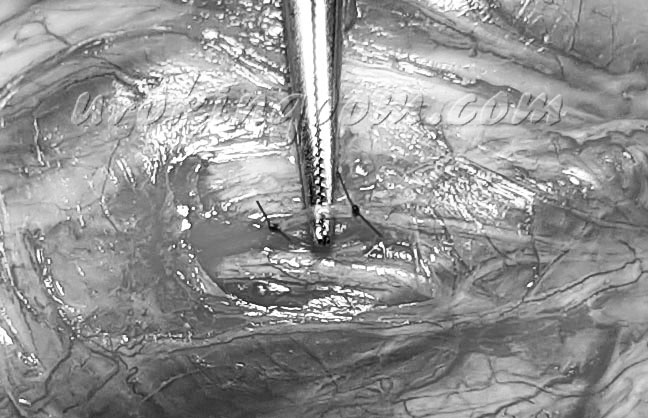
- Using a microscope, selected branches of the dorsal nerve are isolated and ligated with fine sutures (Figure 2)
- Remaining structures are preserved to avoid complications

Our Surgical Advantages
- Dual-local anesthesia: no general anesthesia needed
- Awake and pain-free: patients can use a phone or Bluetooth headset during the procedure
- Single small incision below the glans
- Outpatient procedure: no hospitalization required
- Can be combined with circumcision
- No electrocautery used, minimizing tissue damage and risk of complications such as numbness or erectile dysfunction
- Microsurgical techniques to reduce bleeding and preserve function
We apply the same surgical standards to related procedures:
- Microsurgical circumcision
- Hernia repair
- Varicocelectomy
- Penile venous ligation
- Penile curvature correction
- Penile/testicular prosthesis implantation
- Vasectomy
Surgical Outcomes & Patient Satisfaction
Numerous studies show SDN effectively delays ejaculation while preserving erectile function. Reported success rates range from 80–95%, with increased control and significant IELT extension.
- One study: Mean IELT increased from 1.1±0.9 to 3.8±3.1 minutes (p<0.01)
- Circumcision alone increased IELT by 0.3 minutes
- Success rates by age group: 22–30 years (95.24%), 31–37 (70%), 38–45 (65%)
Other findings:
- Alyaev & Akhvlediani: IELT increased from 53.6±12.7 to 335.6±81.5 sec (6x improvement)
- Korean Sexual Medicine Association: 96.6% patient satisfaction
Possible complications (from various studies):
- Recurrence of PE: 10.2%
- Glans discomfort or altered sensation: 3.8–4.9%
- Erectile dysfunction: 0.4%
- Penile edema: 4.2%
- Wound dehiscence: 2.1%
- Delayed ejaculation: 0.6%
It is essential to balance the number of nerve branches cut to optimize results and avoid loss of penile sensation or erectile issues.
Conclusion
Selective Dorsal Neurotomy offers a viable, long-term treatment for patients with primary premature ejaculation who do not respond to conventional therapies.
Minimally invasive SDN, especially when combined with circumcision, significantly reduces the risk of complications and provides reliable outcomes.
This surgery is a safe and effective choice for men seeking lasting improvement in sexual performance and quality of life. It can also be integrated with other treatment options to maximize results.
期刊論文
- Hsu GL, Hsieh CH (謝政興), Chen HS, Ling PY, Wen HS, Liu LJ, Chen CW, Chua C. The advancement of pure local anesthesia for penile surgeries: can an outpatient basis be sustainable (純粹局部麻醉施行陰莖手術的新進展) Journal of Andrology. 28(1):200-205, 2007.
- Hsu GL, Zaid UX, Hsieh CH (謝政興), Huang SJ. Acupuncture assisted local anesthesia for penile surgeries (針灸輔助局部麻醉下施行陰莖手術). Translational Andrology and Urology. 2(4):291-300, 2013.
- Hsu GL, Hsieh CH (謝政興), Wen HS, Hsu WL, Chen YC, Chen RM, Chen SC, Hsieh JT. The effect of electrocoagulation on the sinusoids in the human penis (電燒止血對於人類陰莖海綿體的影響). Journal of Andrology. 25(6):954-959, 2004.
- Hsu GL, Hsieh CH (謝政興), Wen HS, Hsu WL, Wu CH, Fong TH, Chen SC, Tseng GF. Anatomy of the human penis: the relationship of the architecture between skeletal and smooth muscles (人類陰莖解剖構造:骨骼肌和平滑肌之間的結構關係). Journal of Andrology. 25:426-431, 2004.
- Hsieh CH (謝政興), Liu SP, Hsu GL, Chen HS, Molodysky E, Chen YH, Yu HJ. Advances in understanding of mammalian penile evolution, human penile anatomy and human erection physiology: Clinical implications for physicians and surgeons (了解哺乳類動物的陰莖進化、人類陰莖解剖學和人類勃起生理學方面的進展:對於內外科醫生的臨床意涵). Medical Science Monitor. 18(7): RA118-125, 2012.
- Hsu GL, Hsieh CH(謝政興), Wen HS, Chen YC, Chen SC, Mok MS. Penile venous anatomy: an additional description and its clinical implication (陰莖靜脈解剖構造:附加描述及其臨床意涵). J Androl. 2003; 24: 921-927.
- Hsu GL, Lin CW, Hsieh CH (謝政興), Hsieh JT, Chen SC, Kuo TF, Ling PY, Huang HM, Wang CJ, Tseng GF. Distal ligament in human glans: a comparative study of penile architecture (人類龜頭遠端韌帶:一項比較研究陰莖結構). Journal of Andrology. 26(5):624-28, 2005.
- Yang SSD, Hsieh CH (謝政興), Chang SJ. Effects of circumcision on urinary tract infection and sexually transmitted disease (包皮環切手術對於尿路感染和性傳染疾病的影響). Tzu Chi Medical Journal. 21(3):185-189, 2009.
參考文獻
- Zhang HF, Zhang CY, Li XH, Fu ZZ, Chen ZY. Dorsal penile nerves and primary premature ejaculation. Chin Med J (Engl). 2009 Dec 20;122(24):3017-9. PMID: 20137494.
- Tullii RE. Neurotomy: a new therapeutic technique for primary premature ejaculation. Proceedings of the 4th Asia-Pacific Society for Impotence Research (APSIR). 1993:134-135
- Taylor JR, Lockwood AP & Taylor AJ. (1996) The prepuce: specialized mucosa of the penis and its loss to circumcision. Br J Urol 77, 291–295.
- Zhang SJ, Zhao YM, Zheng SG, Xiao HW & He YS. (2006) Correlation between premature ejaculation and redundant prepuce. Zhonghua Nan Ke Xue 12, 225–227.
- Shi WG, Wang XJ, Liang XQ, Liu ZQ, Huang MJ, Li SQ et al. (2008) Selective resection of the branches of the two dorsal penile nerves for primary premature ejaculation. Zhonghua Nan Ke Xue 14, 436–438.
- Alyaev YG, Akhvlediani ND. Comparing efficacy of selective penile denervation and circumcision for primary premature ejaculation]. Urologiia. 2016;1(suppl 1):60–4.
- Zhang HF, Zhang CY, Li XH, Fu ZZ & Chen ZY. (2009) Dorsal penile nerves and primary premature ejaculation. Chin Med J (Engl) 122, 3017–3019.
- Zhang GX, Yu LP, Bai WJ, Wang XF. Selective resection of dorsal nerves of penis for premature ejaculation. Int J Androl. 2012 Dec;35(6):873-879.
- Yang DY, Ko K, Lee WK, Park HJ, Lee SW, et al. Urologist’s practice patterns including
- Yang DY, Ko K, Lee WK, et al. Urologist’s Practice Patterns Including Surgical Treatment in the Management of Premature Ejaculation: A Korean Nationwide Survey. World J Mens Health. 2013 Dec;31(3):226-31.
- Liu Q, Li S, Zhang Y, Cheng Y, Fan J, Jiang L, et al. Anatomic basis and clinical effect of selective dorsal neurectomy for patients with lifelong premature ejaculation: a randomized controlled trial. J Sex Med. 2019; 16:522–30.
- Yang J, Chu M, Qi Y, Zhang H, Yuan T, Zhou L, Cao W, Zhang C. Correlation between age and curative effects of selective dorsal neurectomy for primary premature ejaculation. Adv Clin Exp Med. 2022; 31(8):837-845.
- Deger MD, Gül M, Serefoglu EC. Surgical treatment of premature ejaculation: a narrative review. Int J Impot Res. 2024; 36(5):474-479.
