手術原理
陰莖勃起時,血液經由陰莖動脈流入左右兩支陰莖海綿體內,造成陰莖海綿體充血膨脹,海綿體外圍繞著堅韌且富彈性的陰莖白膜,同時協助壓迫住陰莖靜脈,讓血液不至於流出陰莖海綿體,才能達到陰莖長度及周徑都增加的堅挺勃起。
不管是任何原因引起的勃起功能障礙,如果其他的治療方法都失效,人工陰莖植入手術就是最終有效的一個治療方式。人工陰莖植入手術就是將人工陰莖體植入陰莖海綿體內,取代充血鼓脹的海綿體,但仍包覆在陰莖白膜內,使陰莖達到足夠的硬度能從事正常性行為,外觀仍與正常陰莖相差無幾,觸感也接近自然。
麻醉方式
傳統上通常採用半身麻醉或全身麻醉方式進行手術。
本院採用新式雙重局部麻醉,包括背神經近枝阻斷術、周陰莖基部組織阻斷術及陰莖腳阻斷術,只在陰莖根部注射局部麻醉藥物(圖一)。手術過程中清醒不會痛,可滑手機、使用藍芽耳機。
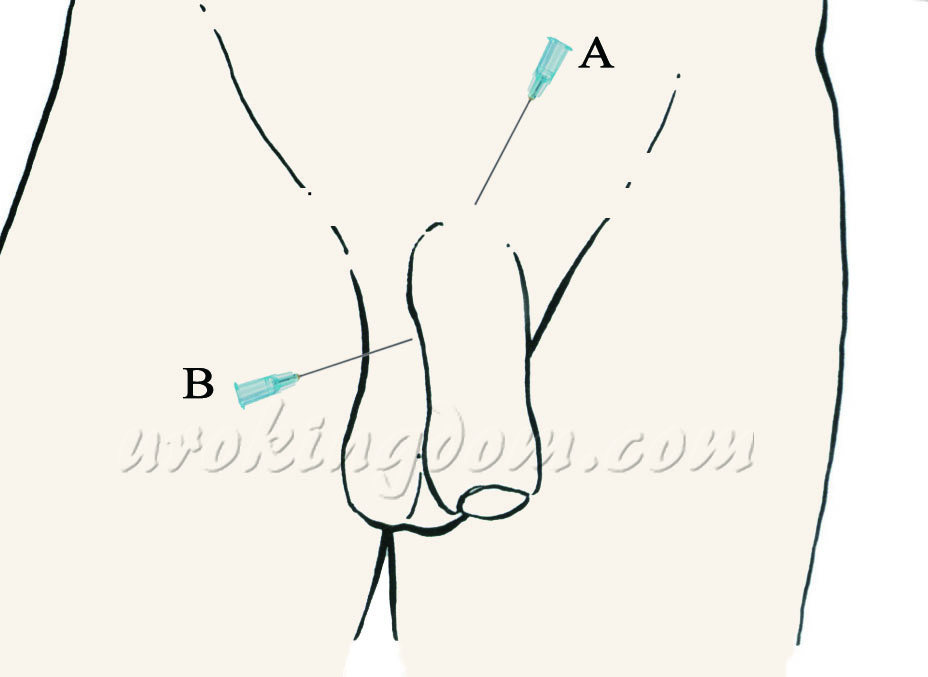
圖一:雙重局部麻醉技術,包括背神經近枝阻斷術、陰莖腳阻斷術(A)及周陰莖基部組織阻斷術(B),只在陰莖根部注射局部麻醉藥物。
手術傷口
龜頭冠狀溝下的包皮環切傷口;恥骨部或陰莖陰囊交界處的單一傷口,大約3公分。
是否需要住院
不需住院! 手術後不需留下觀察,即可自由行走返家休息。
手術方法
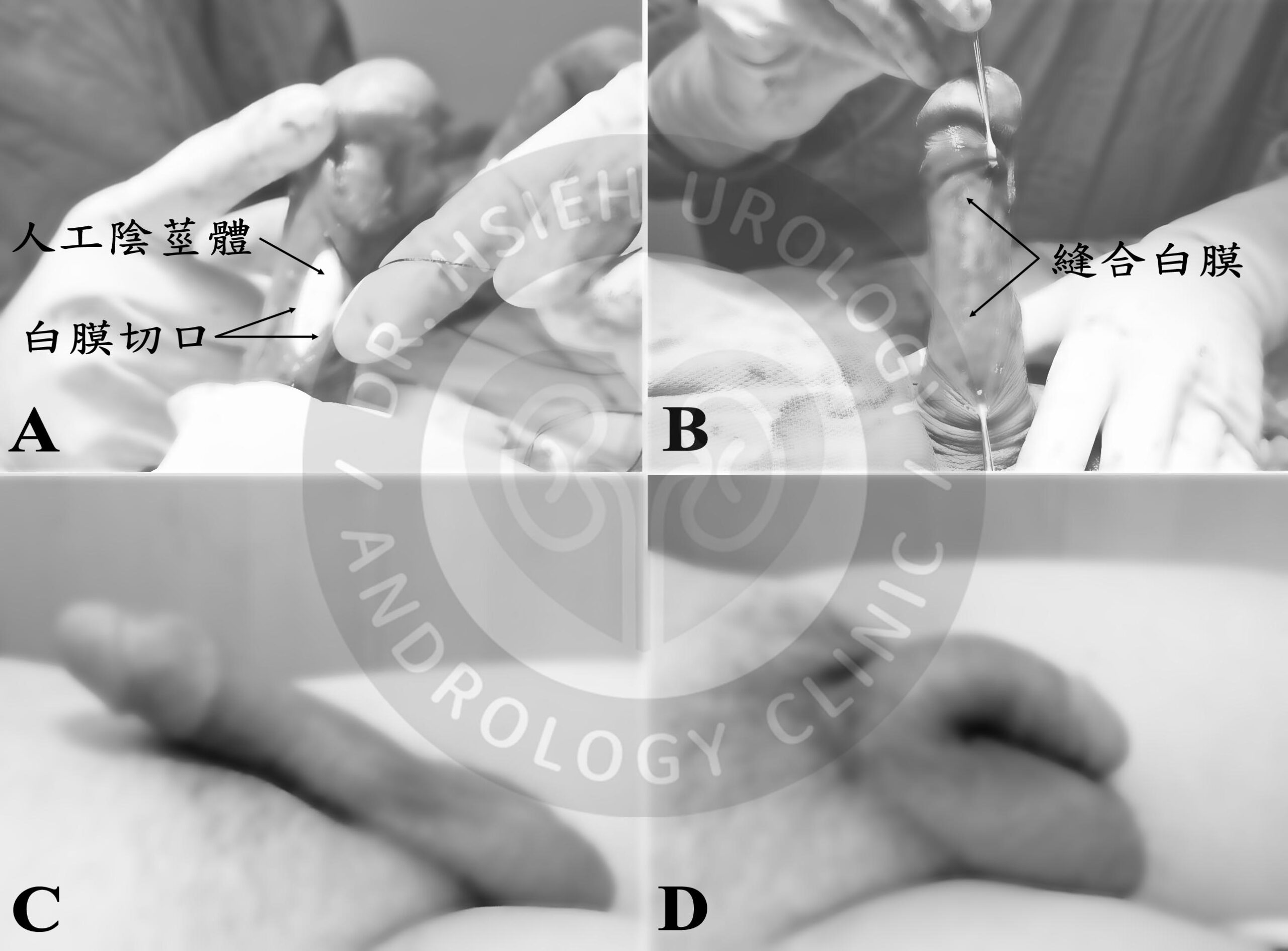
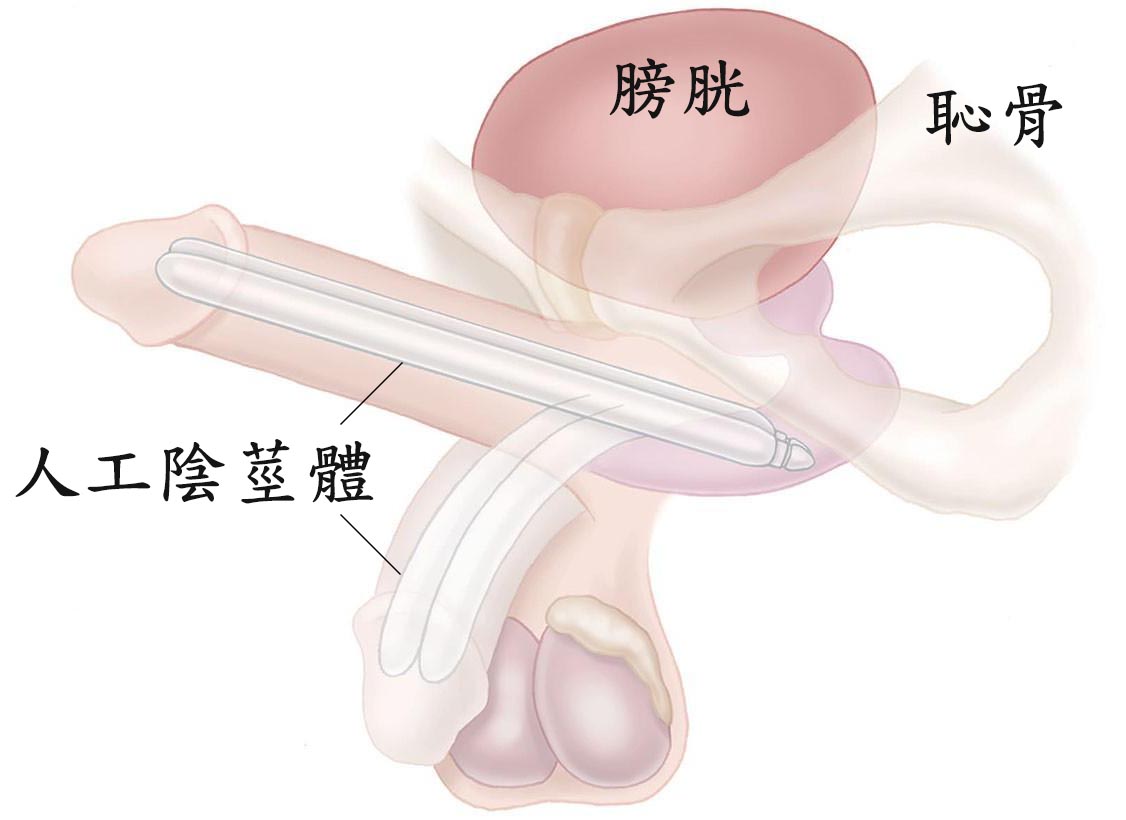
手術採平躺姿勢,在手術部位施行精準的雙重局部麻醉。手術方式因選用不同款式的人工陰莖而有差異,、下恥骨部或陰莖陰囊交界處。應用顯微手術技巧,小心游離傷口內面組織,避免傷害神經及血管,將陰莖白膜與周邊組織分離清楚並切開兩側陰莖海綿體的陰莖白膜。選擇適合長度的人工陰莖體植入兩側陰莖海綿體內(圖二A),再以細小縫線精細縫合白膜切口(圖二B)。如果是是植入非充水式(半硬可折式)人工陰莖,此時即已完成主要的手術步驟,再使用細小縫線分層縫合傷口,並立即以紗布纏繞包紮完成手術。可以用手向上(圖二C)或向下折彎(圖二D)。將前段陰莖向上扳起即可立即進行性行為,性行為後可向下折彎至下垂狀態(圖三)。
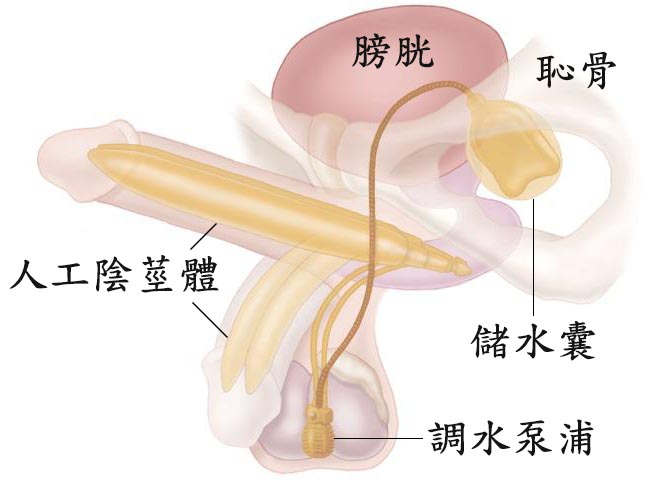
如果是植入三件充水式人工陰莖,另需將調水泵浦植入陰囊中,儲水囊植於恥骨後、膀胱前方的空間,三個物件之間以蜿蜒的管線相連接(圖五)。待人工陰莖物件都妥善植入後,使用細小縫線分層縫合傷口,並立即以紗布纏繞包紮完成手術。擠壓置於陰囊內的調水泵浦,人工陰莖體即可充水勃起,立即進行性行為;擠壓調水泵浦的另一處開關,即可消軟人工陰莖體,回復下垂狀態(圖四)。此項精細的手術出血量極少,手術過程中如偶遇出血點,不使用電燒止血,而使用微細縫線綁紮止血,以避免造成鄰近組織、動脈血管及神經的熱傷害,減少可能的併發症。

本院手術特色
- 雙重局部麻醉
- 單一傷口
- 不需住院!
- 不需電燒止血,組織破壞最少。手術中如遇血管出血而使用電燒止血時,可能傷害到緊鄰近的動脈血管或神經,造成神經感覺異常、麻木感或慢性疼痛;動脈損傷則可能造成局部缺血、有組織壞死的風險。許多醫學文獻報告都指出,使用電燒止血時,局部組織遭到破壞,止血燒焦的地方即無血液循環,對於細菌的抵抗力下降,將增加傷口感染發炎的機率;即使沒有感染發炎,也易影響傷口癒合。
- 應用精細的顯微手術技巧,以詳細了解的陰莖解剖構造作為手術指引,提高手術安全性、減少可能併發症。本院執行其餘相關手術,包括顯微包皮環切手術、疝氣修補手術、精索靜脈曲張手術、改良式陰莖靜脈截除手術、陰莖彎曲矯正手術、人工睪丸植入手術、輸精管結紮手術、陰莖背神經阻斷手術等,均依據以上原則進行,手術相對安全,併發症發生機率極低。
手術預後
由於人工陰莖植入手術是針對重度勃起功能障礙患者,滿意度介於69%到95%之間。國內研究顯示,接受人工陰莖植入手術患者的滿意度高達86.6%,使用非充水式或充水式人工陰莖並不影響滿意度。感染併發症佔5.7%。機械故障率達6.6%,6.0%發生術後陰莖疼痛,局部包皮水腫超過一個月佔5.4%。整體而言,非充水式人工陰莖的5年無故障率較高(84%)。另外根據Wilson等人於2007年所做的針對2384位首次接受充水式人工陰莖植入手術的長期追蹤報告顯示,經過1年的追蹤,人工陰莖無故障率高達90.0%;追蹤5年後的無故障率也仍有79.1%;但是長達10年的追蹤發現充水式人工陰莖的無故障率下降至68.5%,而追蹤15年後更下降至59.7%。
結語
人工陰莖植入手術是治療勃起功能障礙的最後方法,但因不是自然的治療方式,不論非充水式(半硬可折式)人工陰莖或充水式(可膨脹式)人工陰莖都有其一定體積,植入陰莖海綿體中絕不可能隱形而不影響正常陰莖自然的特性,但仍不失為有效治療勃起功能障礙的一項重要選擇,可以保有一線生機,協助恢復正常的性生活,不會影響原有的高潮及射精功能。
註解: 資料來源
- 圖三:https://www.bostonscientific.com/en-US/products/penile-prosthesis/spectra-concealable-penile-prosthesis/features–benefits.html
- 圖五:https://www.bostonscientific.com/content/dam/bostonscientific/uro-wh/general/ams/hcp-resource-center-update/AMS-700-with-InhibiZone.jpg
期刊論文
- Hsu GL, Hsieh CH (謝政興), Wen HS, Chen SC, Chen YC, Liu LJ, Mok MS, Wu CH. Outpatient penile implantation with the patient under a novel method of crural block (以新的陰莖腳局部麻醉方法施行陰莖植入門診手術). International Journal of Andrology. 27:147-151, 2004.
- Hsu GL, Hsieh CH (謝政興), Chen HS, Ling PY, Wen HS, Liu LJ, Chen CW, Chua C. The advancement of pure local anesthesia for penile surgeries: can an outpatient basis be sustainable (純粹局部麻醉施行陰莖手術的新進展)? Journal of Andrology. 28(1):200-205, 2007.
- Hsu GL, Zaid UX, Hsieh CH (謝政興), Huang SJ. Acupuncture assisted local anesthesia for penile surgeries (針灸輔助局部麻醉下施行陰莖手術). Translational Andrology and Urology. 2(4):291-300, 2013.
- Hsu GL, Hsieh CH (謝政興), Wen HS, Hsu WL, Chen YC, Chen RM, Chen SC, Hsieh JT. The effect of electrocoagulation on the sinusoids in the human penis (電燒止血對於人類陰莖海綿體的影響). Journal of Andrology. 25(6):954-959, 2004.
- Hsu GL, Hsieh CH (謝政興), Wen HS, Hsu WL, Wu CH, Fong TH, Chen SC, Tseng GF. Anatomy of the human penis: the relationship of the architecture between skeletal and smooth muscles (人類陰莖解剖構造:骨骼肌和平滑肌之間的結構關係). Journal of Andrology. 25:426-431, 2004.
- Hsieh CH (謝政興), Liu SP, Hsu GL, Chen HS, Molodysky E, Chen YH, Yu HJ. Advances in understanding of mammalian penile evolution, human penile anatomy and human erection physiology: Clinical implications for physicians and surgeons (了解哺乳類動物的陰莖進化、人類陰莖解剖學和人類勃起生理學方面的進展:對於內外科醫生的臨床意涵). Medical Science Monitor. 18(7): RA118-125, 2012.
- Hsu GL, Hsieh CH (謝政興), Chen SC. Human penile tunica albuginea: anatomy discovery, functional evidence and role in reconstructive and implant surgery (人類陰莖白膜:解剖學發現、功能上證據和在重建及人工陰莖植入手術中的角色). Global Advanced Research Journal of Medicine and Medical Science. (GARJMMS) 3(12):400-407, 2014.
- Hsu GL, Hsieh CH (謝政興), Wen HS, Chen YC, Chen SC, Mok MS. Penile venous anatomy: an additional description and its clinical implication (陰莖靜脈解剖構造:附加描述及其臨床意涵). Journal of Andrology. 24(6):921-927, 2003.
- Hsu GL, Wen HS, Hsieh CH (謝政興), Liu LJ, Chen YC. Traumatic glans deformity: reconstruction of distal ligamentous structure (外傷性龜頭畸形:重建遠端韌帶結構). Journal of Urology. 166:1390, 2001.
- Hsu GL, Lin CW, Hsieh CH (謝政興), Hsieh JT, Chen SC, Kuo TF, Ling PY, Huang HM, Wang CJ, Tseng GF. Distal ligament in human glans: a comparative study of penile architecture (人類龜頭遠端韌帶:一項比較研究陰莖結構). Journal of Andrology. 26(5):624-28, 2005.
- Hsu GL, Hill JW, Hsieh CH (謝政興), Liu SP, Hsu C. Venous ligation: a novel strategy for glans enhancement in penile prosthesis implantation (靜脈綁紮手術: 人工陰莖植入手術時增大龜頭的新方法), in Genitourethral Reconstruction, Ralf Herwig R, Sansalone S, Rehder P, Editors. BioMed Research International. Published special issue, Article ID923171, 7 pages, 2014.
- Hsieh CH (謝政興), Hsu GL, Chang SJ, Yang SSD, Liu SP, Hsieh JT. Surgical niche for the treatment of erectile dysfunction (手術治療勃起功能障礙的利基). International Journal of Urology. 27(2):117-133, 2020.
書籍著作
- Cheng-Hsing Hsieh (謝政興)、Geng-Long Hsu (許耕榕). 治療勃起功能障礙 – 手術治療(Erectile Dysfunction – Surgical Management).書名:男性性功能障礙 – 臨床診治全攻略 (Male Sexual Dysfunction – A Complete Guide to Diagnosis and Treatment), 陳煜、簡邦平、蔡維恭、陳卷書編輯. 合記圖書出版社, 2023. 第三篇,第17章,頁245-262.
- Cheng-Hsing Hsieh (謝政興)、Geng-Long Hsu (許耕榕). 勃起功能障礙 – 手術治療 (Erectile Dysfunction – Surgical Treatment). 書名:臨床泌尿學 (CLINICAL UROLOGY). 郭漢崇、賴明坤、楊啟瑞、黃一勝、余燦榮、陳進典、崔克宏,編輯. 台灣泌尿科醫學會, 2012.第八篇,第54章,頁1037-1049.
- Geng-Long Hsu (許耕榕)、Cheng-Hsing Hsieh (謝政興). 書名:A LABORATORY MANUAL FOR POTENCY MICROSURGERY (性功能顯微手術實驗訓練手冊). 許耕榕、謝政興,編輯.
參考文獻
- Goodwin WE, Scott WW. Phalloplasty. J Urol. 1952; 68: 903.
- Beheri GE. Surgical treatment of impotence. Plast Reconstr Surg. 1966; 38: 92.
- Pearman RO. Insertion of a silastic penile prosthesis for the treatment of organic sexual impotence. J Urol. 1972; 107: 802-806.
- Small MP, Carrion HM, Gordon JA. Small-Carrion penile prosthesis: new implant for management of impotence. Urology 1975; 5: 479.
- Finney RP. New hinged silicone penile implant. J Urol 1977; 118: 585-587.
- Jonas U, Jacobi GH. Silicone-silver penile prosthesis: description, operative approach and results. J Urol. 1980; 123: 865-867.
- Scott FB, Bradley WE, Timm GW. Management of erectile impotence: use of implantable inflatable prosthesis. Urology. 1973; 2: 80-82.
- Furlow WL. Inflatable penile prosthesis: Mayo clinic experience with 175 patients. Urology. 1979; 13: 166-171.
- Montague DK. Experience with semirigid rod and inflatable penile prostheses. J Urol. 1983; 129: 967-968.
- Burnett AL, Nehra A, Breau RH, et al. Erectile Dysfunction: AUA guideline. 2018;https://www.auanet.org/guidelines/non-oncology-guidelines/sexual-and-reproductive-health.
- Hellstrom WJG, Montague DK, Moncada I, et al. Implants, mechanical devices, and vascular surgery for erectile dysfunction. J Sex Med. 2010; 7:501-523.
- Wilson SK, Carson CC, Cleves MA, et al. Quantifying risk of penile prosthesis infection with elevated glycosylated hemoglobin. J Urol. 1998; 159:1537–1539. discussion 9–40.
- Chiang HS, Wu CC, Wen TC. 10 years experience with penile prosthesis implantation in Taiwanese patients. J Urol. 2000; 163: 476-480.
- Wilson SK, Delk JR, Salem EA, Cleves MA. Long-term survival of inflatable penile prostheses: single surgical group experience with 2384 first-time implants spanning two decades. J Sex Med. 2007; 4:1074-1079.
- Brant MD, Ludlow JK, Mulcahy JJ. The prosthesis salvage operation: immediate replacement of the infected penile prosthesis. J Urol. 1996; 155: 155-157.
- Mulcahy JJ. Treatment alternatives for the infected penile implant. Int J Impot Res. 2003; 15(Suppl 5): S147-149.

